The Effect of Vitamin D Deficiency on Periodontal Disease
How Vitamin D Deficiency Affects Periodontal Disease
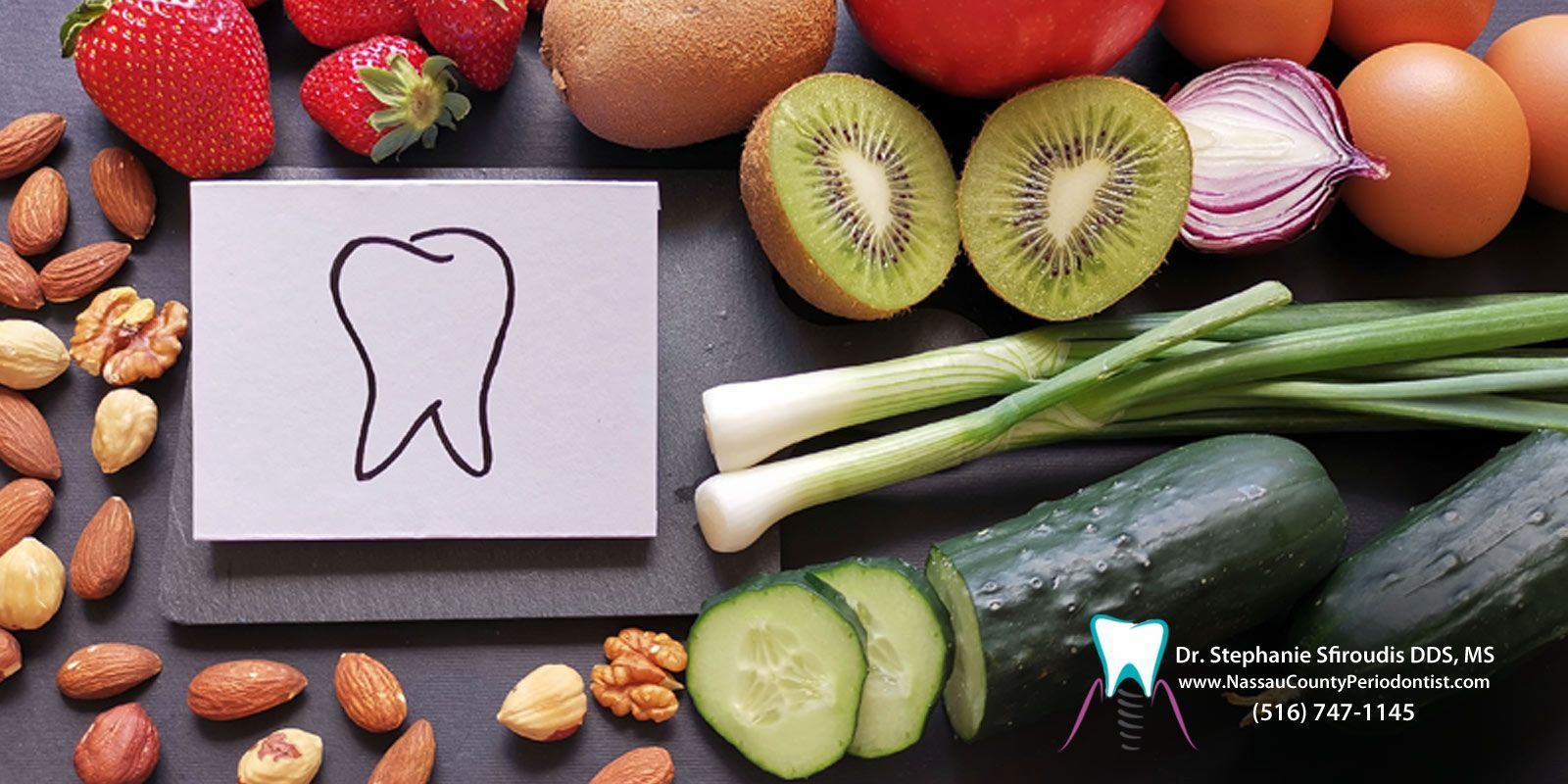

Part of having a healthy mouth is ensuring you receive an adequate amount of vitamin D. When your body is low in vitamin D; it leaves you susceptible to some risks including low mineral bone density and chronic inflammatory diseases, such as periodontal disease , the most common cause of tooth loss in adults.
What is Periodontal Disease?
Periodontal disease, also known as PD, is a persistent gum condition that results from a build-up of bacteria in the mouth. Bacteria cause the gums to become inflamed, redden, and bleed, and over time, cause the connective tissue holding the teeth to become damaged, also known as attachment loss. Left untreated, PD can eat away at the jaw bone and other structures and eventually lead to tooth loss . Certain factors increase your risk of developing periodontal disease, including vitamin D deficiency.
Vitamin D and Periodontal Disease
Vitamin D affects as many as 2,000 genes in the body and aids in the prevention of periodontal disease in the following ways:
Contains Antimicrobial Properties
Vitamin D produces peptides called defensins and cathelicidins, which are natural antibiotics with antimicrobial properties that reduce the amount of bacteria in the mouth. Also, vitamin D also reduces MMPs, or matrix metalloproteinases, the enzymes associated with periodontal disease. A vitamin D deficiency leaves you void of these properties, which can leave you susceptible to developing periodontal disease. According to studies, individuals with lower vitamin D levels experienced more attachment loss than those with higher vitamin D levels.
Maintains Skeletal Integrity
Vitamin D is crucial for the maintenance of skeletal integrity, including the jaw bone, through its role in regulating proper extracellular calcium levels. In fact, research shows that Vitamin D has several anabolic effects on bone formation, including stimulating alkaline phosphate and osteopontin, which is responsible for stimulating bone resorption. Bone resorption is crucial for bone remodeling and formation of new bone, two key factors in maintaining skeletal integrity.
Improves Periodontitis
Vitamin D helps lower the risk of developing periodontitis and helps improve the condition in current sufferers, by maintaining oral health and by exerting anti-inflammatory effects caused by bacteria.
One study on the effects of vitamin D and calcium supplementation on periodontitis found that oral supplementation of vitamin D and calcium improved bone density, decreased debris and tartar found on the teeth, decreased gingival bleeding, decreased pocket depth, and improved tooth stability and bone support in patients with periodontitis. Researchers conclude that vitamin D and calcium supplementation used as an accompaniment can greatly improve treatment outcome.
Sources of Vitamin D
Vitamin D, also known as the "sunshine vitamin," is a group of fat-soluble vitamins, which include D-3, D-2, and D-1. It is naturally found in the body and is produced when the body is exposed to direct sunlight, in as little as 10 minutes for most individuals. Certain foods also contain vitamin D, including:
- Egg yolk
- Shrimp
- Sardines
- Salmon
- Vitamin D fortified foods
- Vitamin D supplements
Causes of Vitamin D Deficiency
Various lifestyle and environmental factors make it difficult to get adequate amounts of vitamin D through the sun alone, including:
- Spending more time indoors
- Pollution
- Living in larger cities where the buildings are shaded from sunlight
- Sunscreen use
- Having darker skin
In cases where these factors are present, it may be necessary to receive some of your vitamin D intake from sources other than direct sunlight.
Recognizing a Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency causes various symptoms in adults, some of which include:
- Severe bone or muscle pain
- Stress fractures
- General tiredness, aches, and pains
Treating a Vitamin D Deficiency
A simple blood test can be performed by your doctor to determine if you are deficient. In addition, your doctor may also schedule an x-ray to observe your bone density. If you are diagnosed with a deficiency, your doctor may recommend certain dietary and lifestyle changes. A daily vitamin D supplement may also be recommended. For a more serious deficiency, high-dose vitamin D liquids or tablets may be advised.
Vitamin D needs vary from person to person; therefore, blood levels should be measured before starting a vitamin D supplement, and then tested again after several months to ensure you are receiving the proper amount.
Please contact Dr. Stephanie Sfiroudis for a free consultation regarding any questions or concerns about vitamin D deficiency or your periodontal health.